Cobalt, a versatile transition metal renowned for its high-temperature stability and exceptional magnetic properties, has garnered significant attention over recent years, primarily due to its critical role in the production of lithium-ion batteries. As the world transitions to renewable energy sources and electric mobility, the demand for cobalt is surging. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive overview of cobalt mining processes, its global distribution, and the major players operating in this industry. dcpipe pipeline expert

Cobalt Mining Processes
The cobalt extraction process is integral to its supply chain and can be divided into several stages: exploration, mining, processing, and refining.
1. Exploration
The first step in cobalt mining is exploration, which involves geological surveys, sampling, and drilling to assess potential cobalt-rich deposits. Geologists look for specific geological formations, particularly those associated with nickel and copper deposits, as cobalt often occurs as a by-product of their extraction. The exploration phase may span several years and includes environmental and feasibility studies to ensure sustainable mining practices.
2. Mining
Once a viable deposit is confirmed, the next step is the mining process, which can be categorized into two primary methods: artisanal mining and large-scale industrial mining.
- Artisanal Mining: This method is prevalent in regions with high cobalt demand, notably in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Artisanal mining involves small-scale operations where individual miners extract cobalt ore using rudimentary tools. This method, while providing livelihoods for many, often leads to unsafe working conditions and substantial environmental degradation.
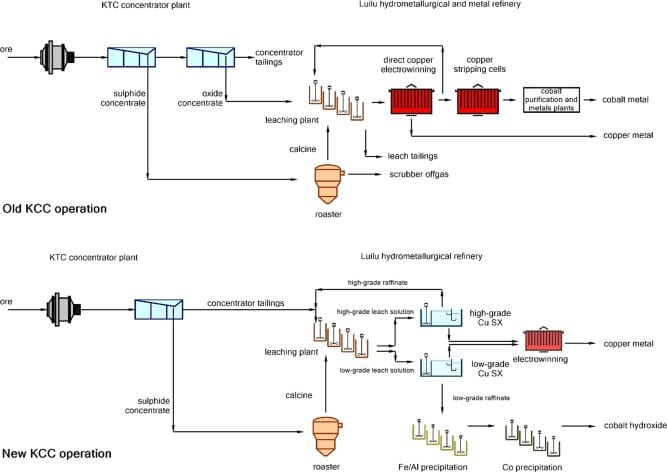
- Large-Scale Industrial Mining: In contrast, industrial mining employs advanced technologies and machinery to extract cobalt from larger deposits. The process typically involves open-pit mining for surface deposits or underground mining for deeper reserves. After ore extraction, it is crushed and subjected to various processes, including flotation, leaching, and hydrometallurgical methods, to recover cobalt.
3. Processing
The processing of cobalt involves several steps to separate it from other minerals and impurities. Common methods include:
- Flotation: This process separates valuable minerals from waste material based on their differing physical and chemical properties. Cobalt is often concentrated alongside copper and nickel.
- Leaching: In cases where flotation is less effective, leaching involves treating the ore with acids or alkaline solutions to dissolve the desired metals, which are then recovered through precipitation.
- Hydrometallurgical Processing: This method is used for extracting cobalt from more complex ores. It involves the use of aqueous solutions to separate metals from the ore, followed by solvent extraction or electro-winning to produce high-purity cobalt.
4. Refining
The final stage in cobalt production is refining, where the concentrate obtained from processing is purified to achieve the desired grade for commercial use. This may involve additional chemical treatments and electro-refining processes, leading to cobalt metal or cobalt salts suitable for battery manufacturing and other applications.
Global Distribution of Cobalt
Cobalt is not evenly distributed across the globe. Its primary reserves are concentrated in a handful of countries, with the DRC being the most dominant player in the cobalt market.
- Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC): The DRC is the world’s largest producer of cobalt, accounting for approximately 70% of global supply. The country’s cobalt is typically extracted as a by-product of copper mining, particularly in the Copperbelt region.
- Australia: Australia is another significant producer, primarily of hard-rock deposits containing cobalt. The country has seen increased investment in mining operations due to rising cobalt prices and demand, particularly from the battery manufacturing sector.
- Canada: Canada has a rich history of mining and is home to several cobalt deposits, including those in Ontario and Quebec. Canadian mining companies often focus on environmentally sustainable practices, making them attractive partners for global markets looking for ethically sourced cobalt.
- Russia: Russia also holds considerable cobalt resources, primarily extracted through nickel mining operations in regions like Norilsk.
- Other countries: Several other countries contribute to global cobalt production, including Cuba, Madagascar, and New Caledonia, although their combined output is significantly lower than that of the DRC and Australia.
Key Mining Companies
Several major companies dominate the cobalt mining landscape, each playing a crucial role in meeting the growing global demand for this essential metal.
- Glencore: As one of the largest commodity trading and mining companies in the world, Glencore operates significant cobalt production facilities in the DRC. The company has committed to responsible sourcing practices and is a member of the Responsible Cobalt Initiative, emphasizing sustainable mining operations.
- China Molybdenum Co., Ltd.: This Chinese company is a major player in the global cobalt market, primarily through its ownership of the Tenke Fungurume mine in the DRC. As the world’s largest cobalt producer, China Molybdenum has been increasing its investment in cobalt resources to support the booming battery industry.
- Norilsk Nickel: Based in Russia, Norilsk Nickel is one of the largest producers of nickel and palladium globally and also extracts cobalt as a by-product. The company has made strides in improving its environmental performance and securing a place in the sustainable mining sphere.
- Axiom Mining: Focused on sustainable mining practices, Axiom is involved in cobalt exploration and production in various regions, placing a strong emphasis on minimizing environmental impact and adhering to ethical sourcing standards.
- Eurasian Resources Group: This company operates in several minerals, including cobalt, and is actively engaged in improving sustainability practices within its operations. Eurasian Resources has made investments to enhance its cobalt production capabilities, particularly in Africa.
Conclusion
Cobalt is a critical mineral in the modern economy, indispensable for the energy transition and the burgeoning electric vehicle market. The mining processes, from exploration to refining, are complex and require careful consideration of environmental and social implications. As the demand for cobalt continues to rise, ensuring sustainable and ethical mining practices has never been more crucial. By focusing on responsible sourcing and fostering innovation in mining technologies, the cobalt industry can pave the way for a more sustainable future while meeting global energy needs. Companies within the industry, such as Glencore and China Molybdenum, are leading this charge, emphasizing the importance of corporate responsibility in light of growing scrutiny over mining practices worldwide. dcpipe pipeline expert

