Salt has been a crucial resource for human civilization since ancient times, serving not only as a flavor enhancer in cooking but also playing a vital role in food preservation, chemical production, and various industrial applications. The mining of salt—referred to as halite in its mineral form—is a significant activity that contributes to the global economy. This blog post delves into the intricate processes involved in salt mining, the geographical distribution of salt deposits, and a brief overview of some prominent mining companies in the industry. dcpipe pipeline expert

Salt Mining Processes
The process of salt mining encompasses various methods, each tailored to specific types of salt deposits and environmental conditions. Below are the primary techniques used in salt extraction:
1. Solution Mining
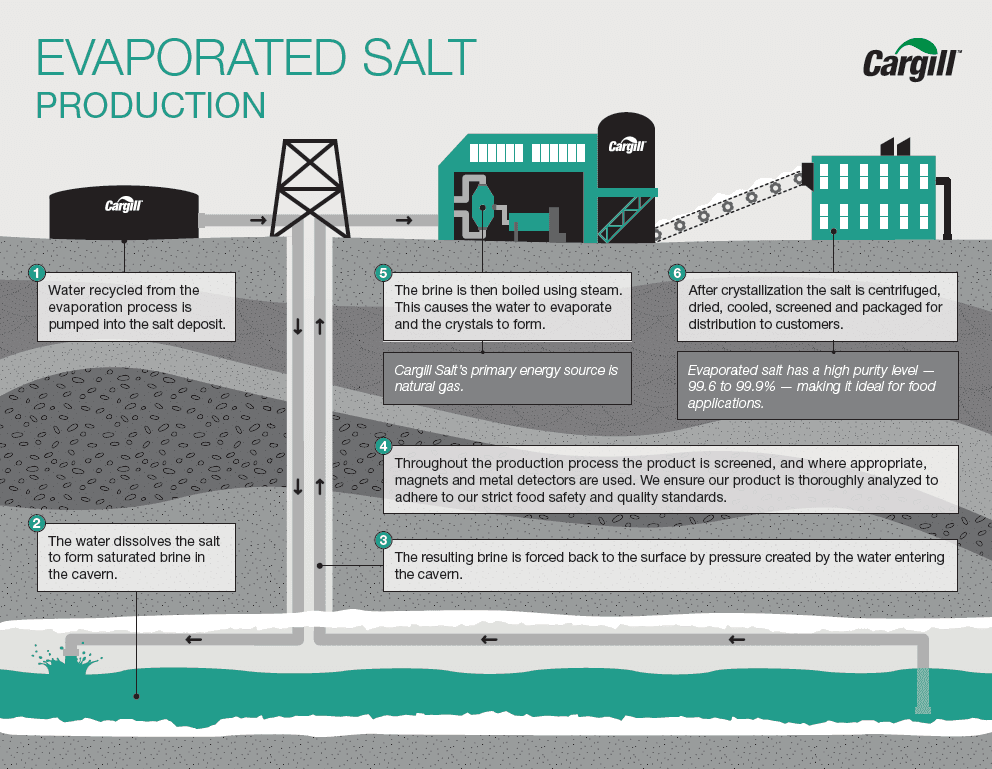
Solution mining is predominantly employed in large underground salt deposits. The process involves drilling wells into underground salt formations and injecting water into the salt layer. This water dissolves the salt, creating a brine solution. The brine is then pumped to the surface, where it undergoes evaporation, typically in large, shallow ponds, to produce crystallized salt.
Advantages:
- Minimal surface disruption compared to traditional mining.
- Ability to access deeper salt deposits that are not feasible for conventional mining.
Disadvantages:
- Potential contamination of groundwater.
- Increased operational costs due to the need for advanced technology.
2. Underground Mining
In regions where salt deposits are located near the surface, traditional underground mining methods are utilized. This method resembles conventional coal or mineral mining, where miners excavate the salt deposit, creating rooms and pillars to support the mine’s structure. Different techniques such as room-and-pillar and cut-and-fill mining may be employed based on the deposit characteristics.
Advantages:
- Direct harvesting of high-purity salt.
- Less water usage compared to solution mining.
Disadvantages:
- More labor-intensive and costly.
- Increased safety risks for miners due to collapse potential and other hazards.
3. Solar Evaporation
In areas with high evaporation rates, solar evaporation is a common method to harvest salt. This approach involves flooding ponds with seawater or brine, allowing the sun and wind to naturally evaporate the water. As the water evaporates, salt crystals form and can later be harvested.
Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly with minimal energy consumption.
- Continuously replenished by tidal movements or nearby sea sources.
Disadvantages:
- Weather-dependent and may lead to inconsistent production levels.
- Lower purity levels compared to mined salt.
Distribution of Salt Deposits
Geographic distribution plays a crucial role in the salt mining industry, as specific regions are known for their rich deposits of salt. Salt deposits are typically found in areas where ancient oceans have evaporated, leaving behind massive salt beds.
1. North America
The United States is home to some of the largest salt deposits, particularly in states like Texas, Louisiana, and Michigan. The Great Lakes region also contains significant marine salt deposits.
2. Europe
Europe has a long history of salt mining, with prominent locations including Germany, Poland, and Austria. The Stassfurt deposit in Germany is particularly well-known for its extensive underground salt mines.
3. Asia
Countries like China and India have substantial salt mining operations, with diverse methods of extraction depending on regional resources. In India, the Rann of Kutch is famous for its natural salt flats.
4. Africa
Africa’s salt production is less extensive but includes noteworthy operations in countries such as Egypt, where salt is harvested from the Mediterranean and Red Sea.
5. South America
In South America, Chile’s Salar de Atacama in the Atacama Desert is known for its extensive solar evaporation operations, producing high-quality lithium and potassium salts alongside sodium chloride.
Leading Mining Companies
The salt mining industry is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and regional companies. Below are some of the prominent players in the industry:
1. K+S Aktiengesellschaft
Based in Germany, K+S is one of the leading salt producers in the world, operating several mines in Europe, North America, and South America. The company offers a comprehensive portfolio of products ranging from table salt to industrial-grade salt and specialty fertilizers.
2. Cargill, Inc.
Cargill is a global conglomerate with a significant presence in the salt mining sector. Operating salt production facilities in the United States, Cargill provides high-quality salt for various applications, including food, agricultural, and industrial sectors.
3. Compass Minerals International, Inc.
An American-based company, Compass Minerals is one of the largest producers of salt in North America. Known for its rock salt and salt products for deicing applications, the company also operates salt mines and solar evaporation facilities.
4. China National Salt Industry Corporation (CNSIC)
As the largest salt producer in China and one of the largest in the world, CNSIC oversees vast operations across the country. The corporation’s extensive portfolio includes table salt, industrial salt, and salt-based chemical products.
5. Saltworks Technologies Inc.
This innovative Canadian company specializes in advanced salt crystal and water evaporation technologies. Saltworks not only produces salt for industrial purposes but also focuses on sustainable water treatment solutions.
Conclusion
Salt continues to be an indispensable resource in modern society, contributing to various industries and applications. The mining processes—from solution mining to solar evaporation—demonstrate the ingenuity behind extracting this vital mineral. As demand for salt escalates, understanding its geographic distribution and the key players in the market will be essential for stakeholders in the industry. As technologies continue to evolve, the future of salt mining promises to become even more efficient and sustainable, catering to the needs of a growing global population while safeguarding our environmental resources. dcpipe pipeline expert

