Open-pit mining, often referred to as open-cast or open-cut mining, is a surface mining technique that involves the extraction of valuable minerals or rocks from the earth by creating a large excavation in the ground. This method is particularly well-suited for minerals and metals that are located close to the earth’s surface and can be mined economically compared to underground mining. While open-pit mining can be highly efficient and profitable, it also carries significant environmental concerns that must be addressed. In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into the definition of open-pit mining, its application in various projects, its advantages and disadvantages, mining methodologies, and its impact on the environment. dcpipe pipeline expert
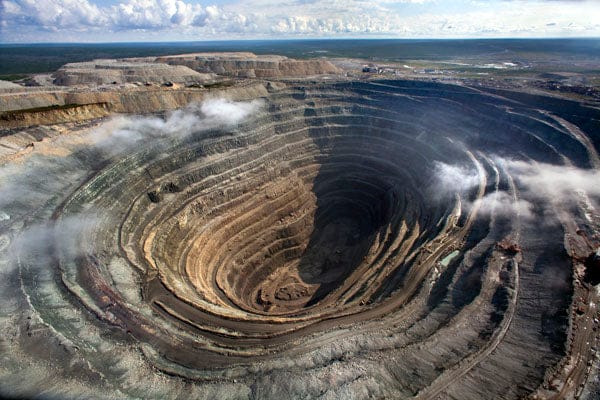

What is Open-Pit Mining?
Open-pit mining is characterized by the formation of a large, terraced pit from which ore can be extracted. The process entails removing overburden—the soil and rock overlaying the mineral deposit—before accessing the desired material. This technique is widely used for the extraction of minerals such as copper, gold, iron, and coal, among others. The open-pit mining process is visually striking, with its expansive pits often visible from aerial perspectives.
Applications of Open-Pit Mining
Open-pit mining is applicable to a variety of projects across different industries. It is particularly advantageous in extracting non-renewable resources found in large concentrations close to the surface. Common projects that utilize this method include:
- Metal Ore Extraction: Open-pit mining is extensively used for metals like copper, gold, and aluminum, where large volumes are required for commercial purposes.
- Coal Mining: In regions where coal deposits are extensive and close to the surface, open-pit methods are frequently chosen for their efficiency.
- Industrial Minerals: Minerals such as limestone, potash, and phosphate are commonly extracted through this method due to their extensive reserves.
- Construction Materials: Sand, gravel, and stone aggregate are often mined via open-pit methods to support construction initiatives.
Advantages of Open-Pit Mining
Open-pit mining presents several advantages that make it a preferred choice for large-scale mineral extraction:
- Cost-Effectiveness: The overall cost of open-pit mining is lower than underground mining due to reduced labor costs and the ability to extract much larger quantities of material simultaneously.
- Higher Production Rates: This method allows for the efficient handling and processing of large volumes of ore, resulting in higher production rates.
- Safety: Open-pit mining tends to be safer than underground mining, where risks such as cave-ins and poor air quality can pose significant threats to workers.
- Accessibility: The surface mining method offers better accessibility to the mined materials, which can simplify the logistics associated with the transport and processing of ore.
- Easier Environmental Monitoring: The environmental impacts of open-pit mining may be easier to monitor compared to underground operations, ensuring stricter compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Disadvantages of Open-Pit Mining
Despite its advantages, open-pit mining poses several significant challenges and drawbacks:
- Environmental Destruction: The process leads to extensive land degradation, habitat destruction, and soil erosion. The removal of overburden can drastically alter the landscape.
- Waste Generation: Open-pit mining produces large amounts of waste material, including tailings, which can create significant disposal challenges and potential contamination risks.
- Visual Impact: The large-scale nature of open-pit mines can negatively impact the aesthetics of the landscape, leading to opposition from local communities and organizations.
- Decreased Biodiversity: The clearing of land destroys local ecosystems, impacting flora and fauna and potentially leading to loss of biodiversity.
Mining Methods in Open-Pit Mining
Open-pit mining employs various methodologies tailored to the characteristics of the site and the materials being mined. Common methods include:
- Bench Mining: This widely used technique involves mining in horizontal layers or “benches.” Each bench is carefully designed to ensure stability while facilitating easy access to the layers beneath.
- Heap Leaching: Often employed in copper and gold extraction, heap leaching involves stacking crushed ore in a heap and applying chemical solutions to extract the metal.
- Block Caving: Although primarily an underground technique, block caving can be applied to some open-pit operations where large volumes of ore can be extracted from an entire block.
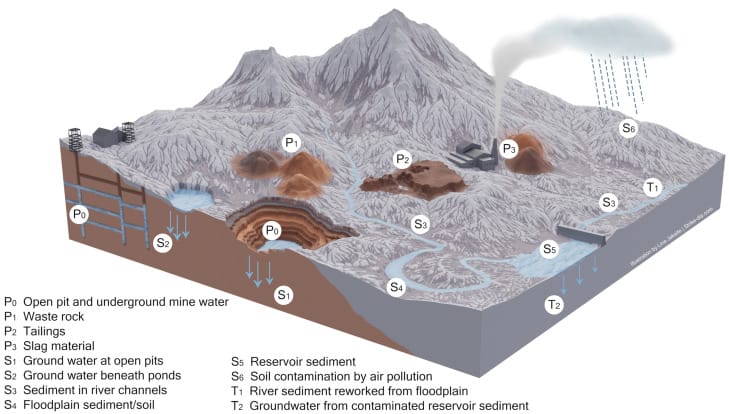
Environmental Impact of Open-Pit Mining
The environmental implications of open-pit mining are manifold and require careful consideration and management. Significant impacts include:
- Habitat Disruption: The removal of vast tracts of land disrupts ecosystems, leading to loss of wildlife habitats and increased vulnerability of species.
- Water Pollution: Mining operations can contaminate groundwater and surface water through runoff and the leaching of toxic chemicals used during extraction processes.
- Air Quality Concerns: Dust and emissions from mining activities can lead to air quality degradation, affecting surrounding communities and ecosystems.
- Long-Term Land Rehabilitation: Although some companies aim to rehabilitate mining sites after closure, the long-term effectiveness of these efforts can vary greatly, necessitating robust planning and commitments.
Conclusion
Open-pit mining is an essential technique within the mining industry that facilitates the extraction of valuable natural resources in an efficient manner. Its applicability across various projects makes it a common choice for mining operations worldwide. However, understanding the advantages and disadvantages, as well as the environmental implications, is paramount to ensure responsible mining practices. As the global demand for minerals continues to rise, balancing economic benefits with environmental stewardship will be crucial in shaping the future of open-pit mining. By implementing sustainable practices and advanced technology, the mining industry can work towards minimizing its ecological footprint while meeting the demands of a burgeoning world economy. dcpipe pipeline expert

