Coal mining is a pivotal component of India’s energy sector, deeply entwined with the country’s economic development and industrial growth. As one of the largest producers and consumers of coal in the world, India’s extensive coal reserves and mining operations are vital to powering its vast industrial base and meeting the energy demands of its growing population. This blog post will provide a comprehensive overview of the coal mining process in India, the distribution of coal mines across the country, and an overview of significant coal mining companies contributing to this sector.

The Coal Mining Process in India
The coal mining process in India typically involves five stages: exploration, extraction, processing, transportation, and reclamation. Each of these stages plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and responsible development of coal resources.
1. Exploration
The first step in coal mining is exploration, where geological surveys and drilling programs are conducted to identify coal deposits. India primarily relies on geological mapping, remote sensing, and geophysical techniques to ascertain the quantity and quality of coal reserves. Extensive laboratory tests are also performed to analyze the coal’s characteristics, including its calorific value, sulfur and ash content, and other essential properties.
2. Extraction
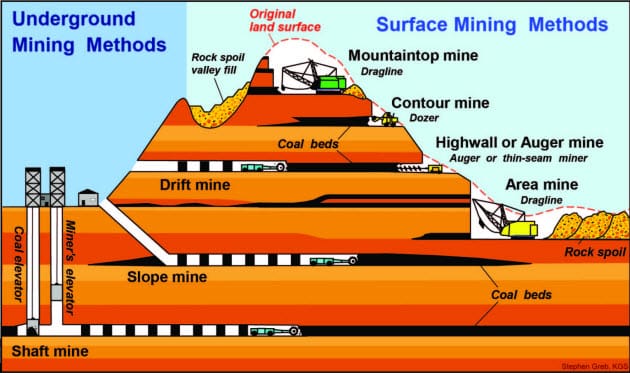
Once a viable coal deposit has been identified, the next phase is extraction, which is conducted through surface or underground mining methods, depending on the depth and location of the coal seams.
- Open-Pit Mining: This method is used for coal deposits near the surface. Large earth-moving equipment is employed to remove the overburden (soil and rock above the coal seam), allowing for direct access to the coal.
- Underground Mining: In cases where coal deposits are located deeper underground, various methods such as room-and-pillar mining or longwall mining are employed. These techniques involve creating tunnels and removing coal while leaving pillars of coal to support the mine structure.
3. Processing
Once coal is extracted, it undergoes processing to enhance its quality and prepare it for transportation. This may include several steps such as crushing, screening, and washing, which remove impurities like sulfur and ash, improving the coal’s calorific value and making it suitable for various industrial applications.
4. Transportation
The transportation of coal from mining sites to end-users is a critical step in the supply chain. India employs a mix of railway networks, waterways, and trucks for coal transportation. The Indian Railways is particularly crucial, as it provides an extensive and efficient rail network that connects major coal-producing regions to industrial centers across the country.
5. Reclamation
Post-mining reclamation is an essential phase aimed at restoring the ecological balance. This process involves rehabilitating mined land, which may include re-vegetation, soil replacement, and the establishment of water bodies. The goal is to mitigate environmental impacts and promote sustainability in mining operations.
Distribution of Coal Mines in India
India boasts one of the largest coal reserves globally, with significant deposits concentrated primarily in the eastern and central regions. The main coal-producing states include:
1. Jharkhand
Home to some of the richest coal reserves in India, Jharkhand is a major contributor to coal production. The renowned Jharia coalfield, known for its high-grade coking coal, is located here.
2. Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh houses substantial coal fields, particularly in the Korba district. The state has witnessed significant investment in coal mining infrastructure.
3. Odisha
Odisha is another key player in India’s coal landscape, with vast reserves located predominantly in the Talcher area. The coal mined here is primarily non-coking.
4. West Bengal
The Raniganj coalfield in West Bengal is one of the oldest coal-producing regions in India. It is known for its substantial deposits of bituminous coal.
5. Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh has sizeable coal reserves, especially in regions like Singrauli, which is crucial for supplying coal to power plants both within and outside the state.
Major Coal Mining Companies in India
A number of companies dominate the coal mining landscape in India, including both public sector undertakings and private players. Some of the most significant coal mining companies include:
1. Coal India Limited (CIL)
As the largest coal-producing company in the world, CIL plays a dominant role in the Indian coal sector. Established in 1975, it operates over 350 mines across eight states and accounts for over 80% of India’s total coal production. CIL has made significant strides in technological advancements and sustainable mining practices, including the implementation of surface mining methods and the adoption of cleaner coal technologies.
2. Singareni Collieries Company Limited (SCCL)
Operating in the southern state of Telangana, SCCL is a major player in the coal industry, known for its underground mining operations. The company has a rich history dating back to 1886 and continues to actively contribute to the local economy and employment generation.
3. Adani Group
The Adani Group has made significant inroads into coal mining and power generation. With a focus on sustainable practices, Adani has invested heavily in developing coal mines in India and abroad, particularly through its Carmichael project in Australia.
4. JSW Energy
JSW Energy has diversified into coal mining to secure its fuel supply for power generation. The company has developed mining operations in various regions and focuses on integrating renewable energy sources alongside its coal-based power generation.
5. Vedanta Limited
A diversified natural resource company, Vedanta has also ventured into coal mining. With its operations prominently in Odisha and Jharkhand, the company is involved in improving the efficiency of coal extraction processes.
Conclusion
The coal mining sector in India is an integral component of the nation’s energy infrastructure, playing a crucial role in driving economic growth and supporting industrialization. While the methods of extraction and processing are becoming increasingly sophisticated, the emphasis on sustainable and environmentally responsible operations is also gaining prominence. As India continues to balance its energy needs with the goals of environmental stewardship, the coal mining industry must adapt to ensure long-term viability and contribute to a sustainable future.
The landscape of coal production is also undergoing significant changes with the increasing focus on renewable energy sources and the gradual transition towards cleaner alternatives. Nevertheless, coal remains and is likely to remain a vital resource for India in the foreseeable future, necessitating continued investment in efficient mining technologies and practices. dcpipe pipeline expert

