Introduction
Mining has been a foundational industry in South Africa, shaping its economy and socio-political landscape for over a century. Among the various mines that play a pivotal role in this sector, South Deep Mine stands out due to its vast reserves of gold, advanced technological integration, and strategic importance. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive overview of South Deep Mine, exploring its history, operations, challenges, and future prospects. dcpipe pipeline expert
History of South Deep Mine
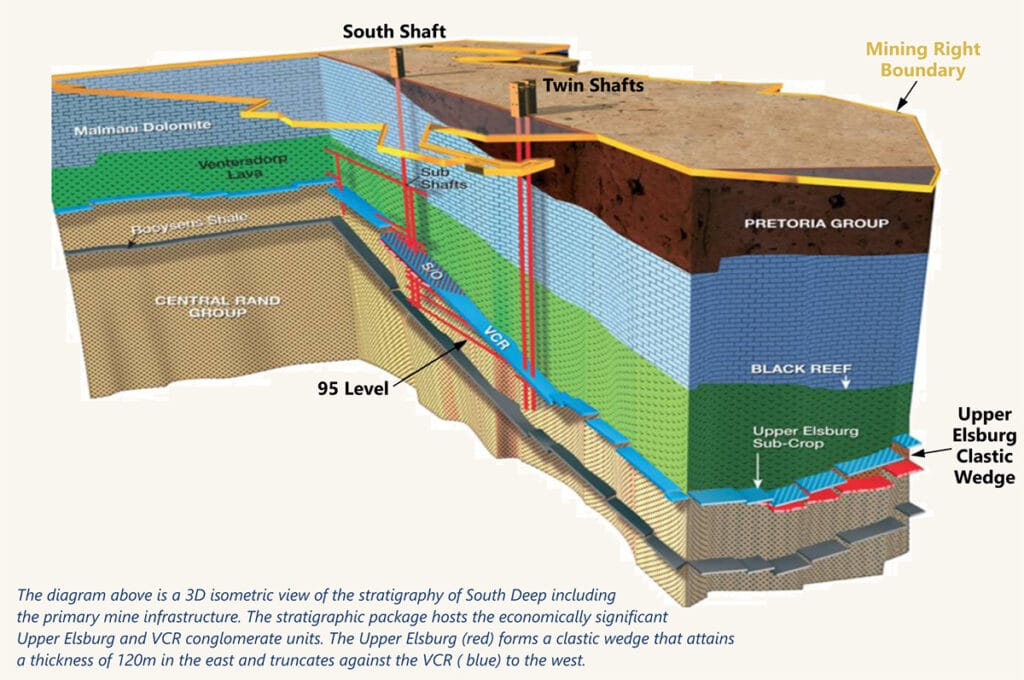
South Deep Mine, located approximately 40 kilometers southwest of Johannesburg, has a storied history that dates back to its establishment in the 1950s. Initially discovered in the 1930s, the mine began production in the late 1980s under the ownership of the former Western Areas Limited. The mine was primarily developed to exploit the vast underground resources of the Witwatersrand Basin, which is renowned for its rich gold deposits.
In the early 2000s, South Deep Mine was acquired by Gold Fields, one of the world’s largest gold mining companies. Under Gold Fields’ stewardship, significant investments were made to modernize the mine, improve extraction techniques, and enhance safety standards. Today, South Deep stands as one of the largest gold mines in the world, boasting an estimated mineral reserve of over 32 million ounces.
Operations and Mining Techniques
Mining Process
South Deep Mine operates using a combination of conventional mining methods and advanced technology. The mine employs a unique method of extraction known as “backfill mining,” which involves filling voids created by the mining process with waste material to ensure ground stability. This method allows for the safe extraction of gold while minimizing environmental impacts.
The mining operations are conducted at depths of up to 3,300 meters below the surface, making it one of the deepest gold mines globally. The mine utilizes two main shafts: the South Shaft and the Twin Shaft, which facilitate the transportation of workers, materials, and ore.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements have played a critical role in enhancing productivity at South Deep Mine. Gold Fields has invested heavily in automation and digital solutions, implementing state-of-the-art systems for monitoring and controlling mining operations. The use of software for geological modeling, ore tracking, and equipment management has improved operational efficiency and safety.
Furthermore, the company has prioritized the integration of sustainable practices within its operations. South Deep has been a leader in implementing renewable energy solutions to reduce its carbon footprint. The use of solar power and waste heat recovery systems has allowed the mine to decrease its reliance on conventional energy sources.
Challenges Faced by South Deep Mine
Operational Challenges
Despite its substantial resources and technological advancements, South Deep Mine faces several challenges. One of the most significant hurdles is the depth of the mine, which presents logistical and operational difficulties. Working at such depths exposes miners to hazardous conditions, including high temperatures and rock falls, necessitating stringent safety measures and protocols.
Additionally, the mine has experienced operational inefficiencies, particularly in the past decade. Issues related to labor relations, productivity, and regulatory compliance have affected output. Gold Fields has recognized these challenges and has implemented a comprehensive turnaround strategy aiming to improve production efficiency and workforce morale.
Economic and Regulatory Challenges
The South African mining industry, including South Deep, is influenced by a complex regulatory environment characterized by stringent labor laws, environmental regulations, and economic policies aimed at promoting local development. Fluctuating gold prices and global economic uncertainties also pose risks to financial sustainability.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, South Deep Mine is poised for growth, driven by several strategic initiatives. The mine’s management is focused on enhancing operational efficiencies through ongoing technological investments. By adopting innovative practices, South Deep aims to achieve its production targets and maintain a competitive edge in the gold market.
Moreover, Gold Fields is committed to social responsibility and community engagement. The mine has established programs aimed at uplifting local communities through skills development, education, and economic opportunities. The focus on corporate social responsibility positions South Deep as a model for sustainable mining practices in South Africa.
Conclusion
South Deep Mine remains a significant player in the global gold industry. With its rich history, advanced operations, and commitment to innovation and sustainability, the mine is well-positioned to overcome its challenges and capitalize on future opportunities. As South Africa continues to evolve as a mining powerhouse, the legacy of South Deep Mine will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of the industry.
The ongoing quest for operational excellence, community empowerment, and environmental stewardship makes South Deep not only a cornerstone of South African mining but also a beacon for sustainable practices in the global mining landscape. For stakeholders, investors, and community members alike, South Deep Mine embodies the potential of modern mining to adapt, innovate, and thrive in the face of an ever-changing world. dcpipe pipeline expert

