Placer mining, often regarded as a fundamental method of extracting valuable minerals from alluvial deposits, has played a pivotal role in the mining industry for centuries. While its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations, placer mining continues to evolve, adapting to modern technological advancements and shifting economic landscapes. This blog post aims to provide a thorough examination of placer mining, covering its history, methods, advantages, challenges, and environmental impact. dcpipe pipeline expert
Understanding Placer Mining
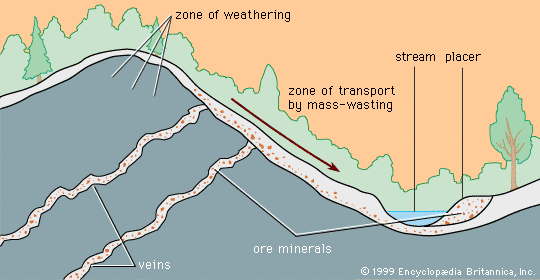
What is Placer Mining?
Placer mining involves the extraction of precious minerals and metals from loose sediments, predominantly found in riverbeds, lakes, or along shorelines. Unlike hard rock mining, which targets primary ore deposits embedded in solid rock, placer mining focuses on the collection of valuable particles that have been naturally weathered and concentrated by water and gravity. Commonly mined materials include gold, silver, platinum, gemstones, and even industrial minerals such as sand and gravel.
Historical Context
The history of placer mining is as rich as the treasures it seeks to unearth. Evidence of early placer mining activities has been found in various cultures around the world, including ancient civilizations in Egypt and Mesopotamia. However, it was during the Gold Rush of the mid-19th century in North America that placer mining gained significant popularity. Adventurers and prospectors flocked to rivers and streams, employing rudimentary tools such as pans and sluice boxes to sift through sediment in search of gold. This rush not only transformed the landscapes of the American West but also had profound social and economic impacts, leading to the establishment of towns and the migration of large populations.
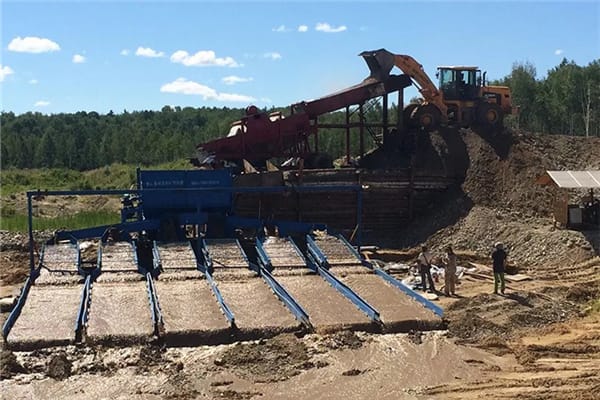

Methods of Placer Mining
Throughout its history, placer mining techniques have evolved significantly. Each method is designed to maximize the recovery of valuable materials while minimizing environmental degradation.
1. Panning
Panning is the simplest and most traditional method of placer mining. This technique involves filling a shallow pan with sediment from a riverbed, adding water, and gently shaking it. As the lighter material is washed away, denser minerals, such as gold, settle at the bottom. While panning requires minimal equipment and can be done by individuals, it is labor-intensive and often yields small quantities of minerals.
2. Sluicing
Sluicing builds upon the principles of panning but utilizes a longer, narrow trough called a sluice box. The box is constructed to allow water flow and is lined with riffles or barriers that trap heavier particles as lighter materials are carried away. This method allows for processing larger quantities of sediment compared to panning and can yield higher volumes of recoverable minerals.
3. Dredging
Dredging involves the use of specialized equipment to extract sediment from underwater deposits. Dredges can be mounted on barges or operated from the shore, using suction or mechanical scoops to collect material. This method is efficient for large-scale operations and can significantly increase mineral yields. However, it often poses greater environmental risks due to the disturbance of aquatic ecosystems.
4. Hydraulic Mining
Hydraulic mining employs high-pressure water jets to dislodge minerals from sediments, directing the flow through sluice boxes for collection. Although this technique can be highly effective in accessing deeply buried deposits, it has faced considerable opposition due to its destructive impact on landscapes and waterways, leading to sedimentation and pollution.
Advantages of Placer Mining
Placer mining offers several advantages that contribute to its longevity as a preferred extraction method.
Resource Recovery
One of the primary benefits of placer mining is its ability to recover valuable resources from sediment deposits with relative efficiency. The concentration of minerals in placer deposits often results in a higher yield compared to traditional mining methods.
Accessibility
Placer deposits are often located in accessible areas, making it easier for miners to reach them without extensive excavation. This accessibility allows for smaller operations and encourages artisanal mining practices, empowering local communities to participate in the mining sector.
Lower Capital Investment
Compared to hard rock mining, placer mining typically requires lower initial capital investments. Individual prospectors and small-scale miners can enter the field with minimal equipment, making it an attractive option for those seeking economic opportunities.
Challenges of Placer Mining
Despite its advantages, placer mining is not without challenges. Understanding these hurdles is crucial for responsible mining practices.
Environmental Impact
One of the most significant concerns surrounding placer mining is its environmental impact. Large-scale operations can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and increased sedimentation in rivers and streams. The disruption of ecosystems can have devastating effects on local flora and fauna, prompting calls for stricter regulations and sustainable practices.
Resource Depletion
Unlike hard rock mining, where substantial reserves may exist, placer deposits can be ephemeral and quickly exhausted. Over-mining can lead to resource depletion, posing long-term challenges for both miners and local economies reliant on these resources.
Regulatory Barriers
As awareness of environmental issues has grown, governments and regulatory bodies have imposed stricter regulations on placer mining activities. Navigating these regulations can be complex and may limit the operational scope for miners, especially smaller-scale operations.
Conclusion
Placer mining, with its rich historical roots and continued relevance in the extraction of precious minerals, remains a prominent aspect of the mining industry. While it offers significant advantages, such as resource recovery and accessibility, the challenges associated with environmental impact and regulation require careful consideration.
As the mining sector continues to evolve, there is a pressing need for innovative approaches that balance resource extraction with sustainability. Emphasizing responsible mining practices and engaging local communities will be essential in ensuring that placer mining can thrive without compromising the integrity of the ecosystems it relies upon.
In navigating its complexities, both industry stakeholders and regulators must work collaboratively to develop frameworks that promote sustainable methods, ensuring that the legacy of placer mining can contribute positively to future generations. dcpipe pipeline expert

